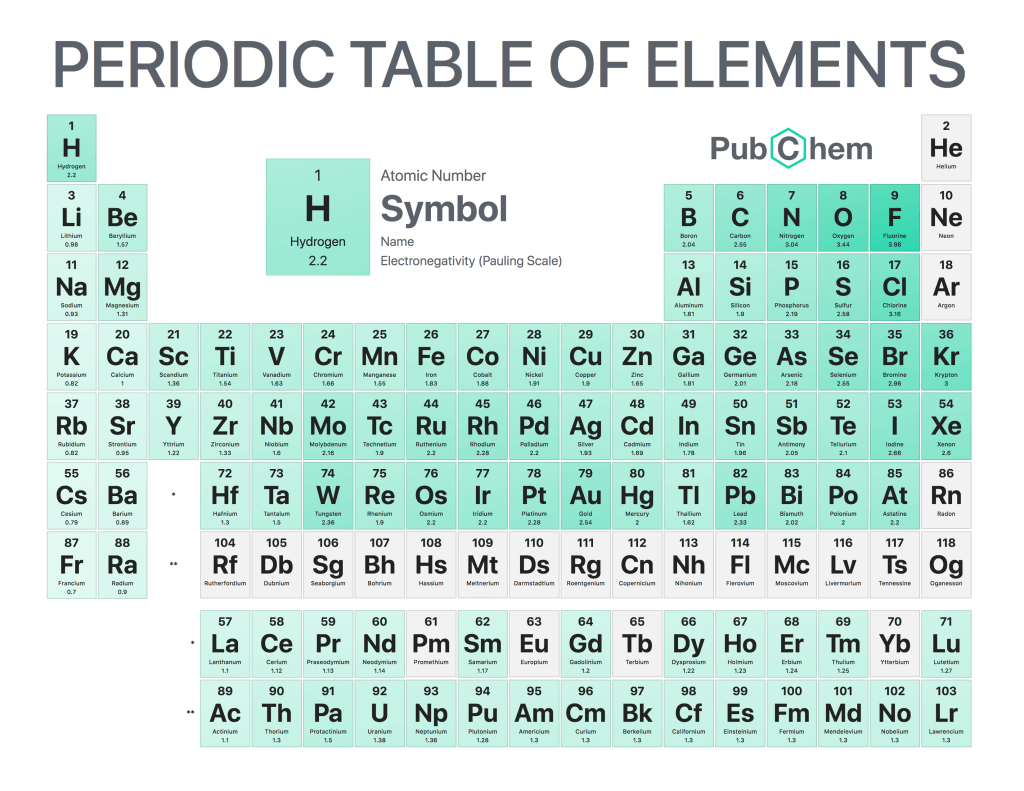
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes how strongly an atom or molecule attracts electrons from another atom. It is the ability of an element to attract shared electrons when it forms a bond with another element. Electronegativity values are determined by measuring the strength of the electrostatic attraction between two atoms in a covalent bond and comparing them to each other on what’s known as the Pauling scale. The higher electronegative value indicates greater electron-attracting power and stronger bonds formed with other elements; conversely, lower electronegativities indicate weaker electron-attracting powers and weaker bonds formed with other elements.
The most common application for electronegativity in chemistry involves understanding how different molecules interact or react together during chemical reactions such as combustion or acid/base reactions – which makes it a very useful tool for predicting reaction outcomes ahead of time. For example, if we know that one molecule has high electronegative values compared to others then we can predict that this particular molecule will be more likely to form strong covalent bonds than its counterparts due to its increased ability to attract electrons away from them during the bonding process (i). Similarly, knowing the relative differences between various molecules’ electronegativity also helps us understand why some compounds may dissolve easily while others remain intact under the same conditions – since solubility often depends on differences in polarity created by unequal sharing of electrons among constituents (ii).
Finally, knowledge about individual atoms’ electronegativity allows scientists to make informed decisions while constructing complex molecular structures like drugs used for medical treatments – since they need to ensure optimal balance between stability & reactivity within the drug’s structure so it could effectively perform the desired function without causing any additional harm(iii). In short, by providing information about relative strengths & weaknesses associated with atomic interactions, electronegativity plays an essential role both in understanding fundamental principles behind chemistry& creating new materials needed for modern-day technologies.
In conclusion, Electornegtivity provides valuable insights into the nature & behavior of matter at the subatomic level – making possible development applications ranging from medicine all way up to space exploration. As a result, this powerful concept remains an indispensable part of science even more than a century after being initially proposed.
